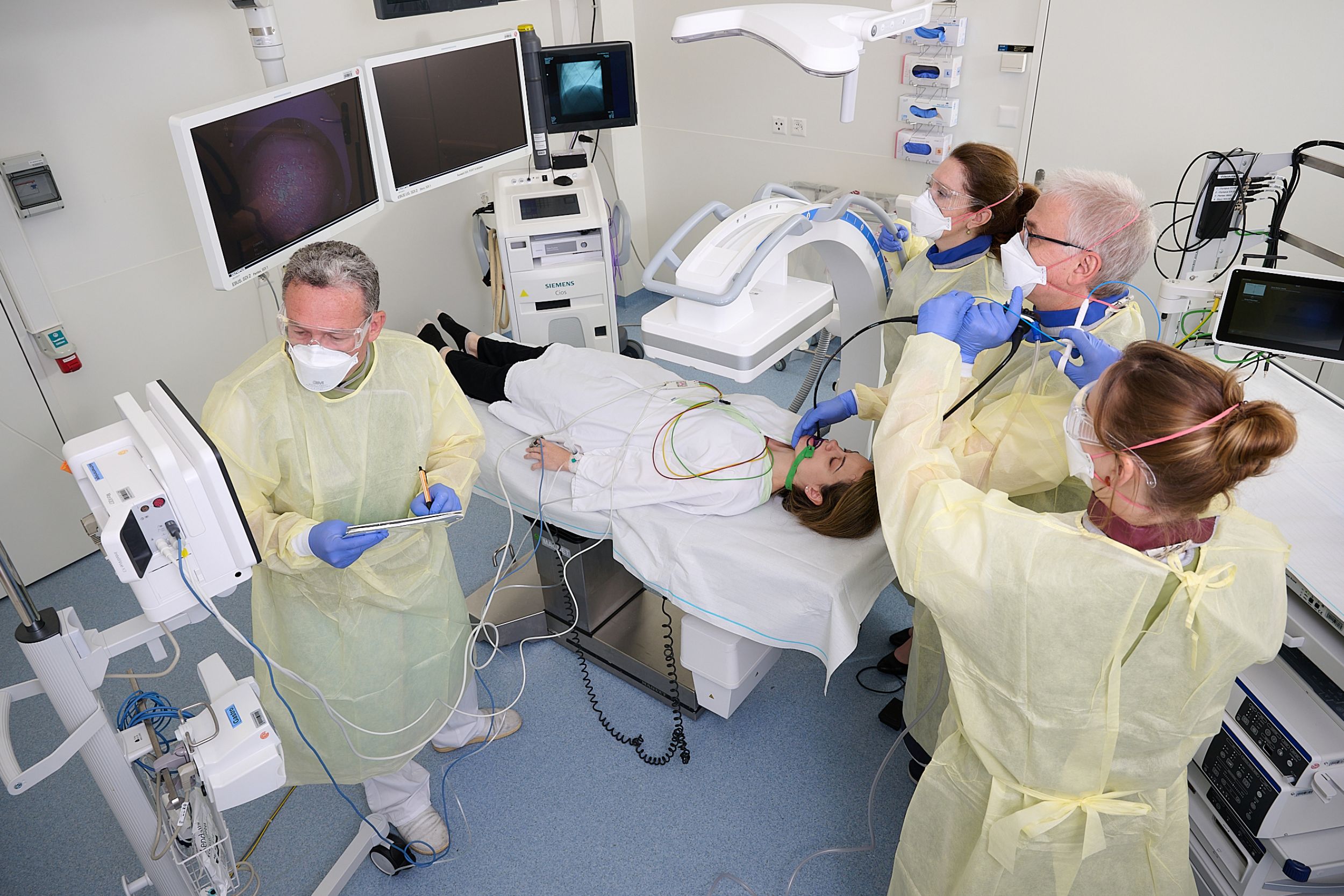
Offer
Cutting-edge medicine across all disciplines
With its combined expertise, experience and regular interdisciplinary conferences, the Lung Center can examine patients with lung diseases quickly and competently and suggest the best treatment for them.
Many years of experience and new scientific findings are incorporated into every treatment of patients with lung disease, as are the advantages of interdisciplinary consultations, which are held regularly at case conferences (IFC). This is where treatment decisions are coordinated between the specialist disciplines. For patients, this interdisciplinary exchange also means the certainty that their situation has been assessed from very different perspectives. Diseases that are not currently in the foreground are taken into account, as are the patient's resources and wishes.
The Lung Center consists of 8 segments, each of which includes different specialists depending on the area of expertise required. The Lung Center attaches particular importance to prompt information. Patients are informed of the recommendations of the interdisciplinary case conference, as are the family doctor and the follow-up doctors involved in the treatment process. In 2021, over 1500 complex cases were discussed at these interdisciplinary conferences. Registrations for interdisciplinary conferences are made via the doctors involved. Patient registrations for special consultations are made via the respective clinics.
Diagnoses
Asthma/COPD
Asthma and COPD are very common diseases, affecting hundreds of thousands of Swiss people. New biologics are now available for severe asthma. As nasal polyps and allergies often also play an important role in these patients, these patients are discussed in the presence of pulmonologists, allergists and ENT specialists. In advanced COPD, bronchoscopic and surgical methods of lung volume reduction are now available; the decision as to which method is most suitable for the individual patient is made together with pulmonologists, thoracic surgeons, radiologists and nuclear medicine specialists.
Lung tumors
The lung tumor segment of the Lung Center is also an important partner of the University Tumor Center. The combination of different specialist disciplines forms the Center for Lung Tumors, within which all patients with lung cancer and other tumors in the area of the chest are treated. Experts from pneumology, thoracic surgery, oncology, radiation oncology, pathology, radiology and nuclear medicine take part in the weekly tumor conference. The combined expertise of various disciplines from the diagnostic and therapeutic spectrum enables rapid clarification and personalized therapy. This also applies to patients from the rest of north-western Switzerland, including the Jura: experts from oncology and pneumology at the Hôpital du Jura in Delémont take part in the meeting every week.
Breathing and sleep disorders
The University Sleep Center is certified together with the University Hospital Basel (USB), the University Children's Hospital Basel (UKBB) and the University Psychiatric Clinics (UPK). The necessary sleep examinations are carried out at all three locations. Complex cases are discussed at the interdisciplinary conference, which is attended by pulmonologists, neurologists and psychiatrists from the various clinics.
Lung infections
Lung infections have not only been common since COVID-19, but also affect immunocompromised patients in particular. In addition to rapid diagnosis, interdisciplinary management plays an important role in protracted infections. Accordingly, pulmonologists, infectious disease specialists, thoracic surgeons and radiologists take care of the optimal treatment proposals.
Interstitial lung diseases
Interstitial lung diseases are associated with an increase in inflammatory cells and connective tissue in the lungs. There are many different causes, such as sarcoidosis or rheumatic diseases. In addition to the diagnostic classification, the therapy concepts are often based on analyzed cells and lung tissue, which is why pathologists regularly participate alongside pulmonologists and radiologists. If necessary, rheumatologists, cardiologists, neurologists and ophthalmologists are also consulted.
Cystic fibrosis and transplantation
The USB and UKBB are European-certified specialist centers for cystic fibrosis, which is the most common genetic lung disease. In addition to new therapies, lung transplantation is also an option for advanced cystic fibrosis. The most common other indications for lung transplantation are advanced COPD and pulmonary fibrosis.
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (pulmonary hypertension) occurs when the blood experiences more resistance through the pulmonary vessels. In addition to investigating the cause, a right heart catheter is needed to determine the exact extent of the disease and initiate treatment. Close collaboration between pulmonologists is essential. As patients with rheumatic diseases often develop pulmonary hypertension, there is also close cooperation with rheumatologists.
Thoracic trauma
Thoracic trauma is an injury to the chest and/or lungs. In addition to the diagnosis, which requires a computer tomogram, surgical rib fixation options are now available.
The lungs at the center
Patients with chronic or acute lung diseases are treated and monitored by specialists at the Lung Center. From a suspected diagnosis to a confirmed diagnosis and treatment. Regardless of whether the patient's treatment is carried out on an outpatient or inpatient basis: Everyone suffering from a lung disease is in the right place here.
Everything under one roof
Because the University Hospital unites all specialist disciplines under one roof, patients can be referred quickly to other specialist areas or for examinations, and the path to these is short.
A comprehensive network
Patients can also feel supported with their worries about their illness. Psychological support is available to them in the form of psycho-oncology . Furthermore, a close-knit network ensures - where necessary and desired - follow-up care or rehabilitation in order to guarantee a good recovery.
